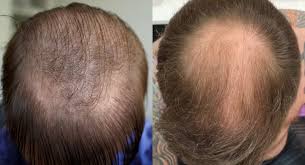
Hair loss can be a distressing experience for many, but with advancements in medical technology, options like hair transplants have provided lasting solutions. However, the journey to full, healthy hair doesn’t end after a transplant. Post-transplant care is crucial, and some patients turn to medications like Finasteride to enhance the results and prevent further hair loss. In this article, we’ll explore whether Finasteride helps after a hair transplant, how it works, and its potential benefits and risks.
Introduction: Understanding Hair Transplants and Finasteride
Hair transplants are a popular and effective solution for individuals suffering from male and female pattern baldness. The procedure involves relocating healthy hair follicles from a donor area to areas of thinning or baldness, offering a permanent way to restore hair. But hair transplant results can vary, and that’s where Finasteride, a medication often prescribed to treat hair loss, comes into play.
Finasteride is commonly used to treat male pattern baldness and works by inhibiting the hormone DHT (dihydrotestosterone), which is responsible for hair follicle shrinkage. Post-transplant, it’s important to know whether Finasteride can further enhance hair regrowth, reduce hair loss, and improve the overall results of the transplant. This article will provide a detailed explanation of how Finasteride works and whether it’s effective after a hair transplant.
How Hair Transplants Work
Hair transplants involve harvesting hair follicles from a donor area (usually the back of the scalp) and implanting them into areas where hair has thinned or disappeared. There are two main techniques:
- FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction): Individual hair follicles are extracted from the donor site and transplanted to the thinning areas.
- FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation): A strip of skin is removed from the donor site, and the hair follicles are then dissected and transplanted.
The transplanted hair is permanent, as the follicles from the donor area are genetically resistant to hair loss. Over time, the transplanted hair will grow, but this process requires patience, as it can take several months for visible results. However, even after a transplant, other areas of the scalp might continue to experience hair loss, which is why many patients use medications like Finasteride to help prevent further thinning.
What is Finasteride in Hair Transplant ?
Finasteride is an oral medication primarily prescribed for the treatment of hair loss, particularly male pattern baldness (androgenetic alopecia). It works by blocking the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, which is responsible for converting testosterone into DHT. DHT is a hormone that contributes to the shrinking of hair follicles, leading to hair thinning and eventual hair loss. By reducing DHT levels, Finasteride helps prevent the miniaturization of hair follicles and can encourage new hair growth.
How Does Finasteride Work?
Finasteride reduces the amount of DHT in the scalp, which can:
- Prevent hair follicle shrinkage: This helps to preserve existing hair and prevents further hair thinning.
- Stimulate hair growth: By reducing DHT, Finasteride may encourage hair follicles to produce thicker and stronger strands.
The medication is typically taken in pill form, with doses ranging from 1mg to 5mg. It is widely used by men but can also be prescribed for women, especially in cases of post-menopausal hair thinning.
Does Finasteride Help After a Hair Transplant?
The answer to whether Finasteride helps after a hair transplant is yes, it can. Finasteride is often recommended after a hair transplant to improve the overall results and prevent further hair loss in other areas of the scalp. Here’s how it works post-transplant:
Benefits of Finasteride Post-Transplant
Prevents Continued Hair Loss: While hair transplanted from the donor site is resistant to hair loss, surrounding hair may continue to thin over time. Finasteride helps reduce the risk of hair loss in areas that are not treated during the transplant.
Enhances Transplant Results: Finasteride can support the transplanted follicles and improve the overall density of hair growth. It promotes healthier follicles by maintaining a healthy scalp environment, encouraging the transplanted follicles to thrive.
Accelerates Hair Growth: Finasteride can stimulate the growth of finer, weaker hair that may still be present in the recipient area. It may also promote the thickening of existing hair in the transplanted zones, leading to denser hair.
Long-Term Benefits: By inhibiting DHT, Finasteride ensures that hair loss does not progress beyond the transplant site. This offers long-term benefits, as it can help to preserve the results of your transplant for many years.
Finasteride and New Hair Growth
Post-transplant, new hair growth typically begins around three to four months after the procedure, with full results visible after 12 to 18 months. By using Finasteride, this process can be enhanced, as the medication works to stimulate hair follicles in their resting phase and promote the growth of new, thicker hair. While Finasteride won’t accelerate the initial shedding phase after a transplant, it can help ensure that the transplanted hair grows as expected and that surrounding hair remains strong and healthy.
The Role of Finasteride in Preventing Hair Loss transplant
One of the key roles of Finasteride after a hair transplant is its ability to prevent further hair loss in areas that were not treated during the transplant. Male pattern baldness is progressive, and even if you have a transplant, you may continue to experience thinning hair in untreated areas.
By taking Finasteride after the procedure, the medication can:
- Slow down hair loss in the crown, temples, or frontal regions.
- Protect existing hair from DHT damage.
- Prevent the progression of baldness, ensuring that the results of the transplant last longer.
For many patients, this is one of the most compelling reasons to use Finasteride after a transplant—helping to preserve the newly transplanted hair and ensuring that the overall appearance remains youthful and thick.
Potential Side Effects of Finasteride Hair Transplant
Like all medications, Finasteride comes with a potential risk of side effects. Some people may experience adverse reactions, although they are rare. The most common side effects include:
- Decreased libido or sexual dysfunction
- Erectile dysfunction
- Reduced semen volume
- Breast tenderness or enlargement in men
These side effects usually subside after discontinuing the medication. However, it’s important to consult with your doctor if any side effects persist. Finasteride is generally well-tolerated, but individuals with specific health concerns should discuss the potential risks with their healthcare provider before starting the medication.
When to Start Using Finasteride After a Hair Transplant
The timing of when to start Finasteride after a hair transplant is crucial for its effectiveness. Most surgeons recommend waiting until the initial healing phase is complete before beginning Finasteride. This generally means waiting about 3 to 6 months after the transplant to ensure the scalp is fully healed and the transplanted hair is securely in place.
Once your doctor gives the go-ahead, starting Finasteride at the right time can significantly improve the outcome of your transplant and prevent further hair loss in untreated areas.
Finasteride vs. Other Post-Transplant Treatments Hair Transplant
While Finasteride is one of the most common medications prescribed after a hair transplant, there are other treatments that can complement its effects. Some of these include:
- Minoxidil (Rogaine): A topical solution that stimulates hair growth and thickens hair. It can be used in combination with Finasteride to enhance results.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: A treatment in which platelets from your own blood are injected into the scalp to stimulate hair growth.
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): A non-invasive therapy that uses light to stimulate hair follicles and promote growth.
Combining Finasteride with these treatments can offer the best results for those seeking optimal hair regrowth post-transplant.
Success Stories: Real-Life Experiences Hair Transplant
Many patients have successfully used Finasteride after their hair transplants to maintain and enhance their results. Success stories often include thicker, fuller hair that looks natural and grows consistently over time. By starting Finasteride after the transplant and following a proper hair care routine, individuals have been able to keep their hair healthy and enjoy long-lasting results.
Conclusion: Should You Use Finasteride After a Hair Transplant?
Finasteride can be a highly effective addition to your post-transplant care routine. It helps not only with maintaining your transplanted hair but also with preventing further hair loss in untreated areas. With its ability to reduce DHT levels and promote hair follicle health, Finasteride can significantly improve the results of your hair transplant.
However, it’s essential to consult with your doctor before starting Finasteride to ensure it’s the right option for you and to monitor any potential side effects. By incorporating Finasteride into your post-transplant regimen, you can maximize the success of your hair restoration journey, ensuring that your new hair grows thick, healthy, and strong for years to come.
