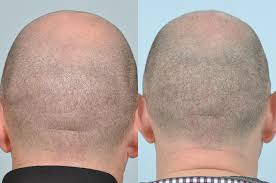
Hair loss is a common concern for many people, but it can be especially impactful for transgender individuals. Gender dysphoria often involves a mismatch between a person’s assigned gender at birth and their gender identity, which can extend to physical traits such as hair growth. For transgender women (assigned male at birth) and transgender men (assigned female at birth), hair loss or the desire to alter their hairline can be a source of distress. Hair transplant procedures offer an effective solution, but it’s essential to understand what to expect, the options available, and how it aligns with the unique needs of transgender patients.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various aspects of hair transplants for transgender individuals, covering the procedure, preparation, recovery, and how it fits within the broader context of gender-affirming care.
Introduction: Understanding Hair Loss in Transgender Individuals
Hair loss can be a common issue for transgender individuals, just like it is for many other people. For transgender men and women, hair loss may happen for different reasons, such as changes in hormones or genetics. For transgender men, taking testosterone can sometimes cause thinning or loss of hair, while transgender women may experience hair thinning because of lower levels of estrogen. It’s important to understand that hair loss is a normal part of life for many people, and there are treatments available to help. Doctors and specialists can guide transgender individuals to the right solutions to manage hair loss.
Transgender Women (Assigned Male at Birth): For transgender women, the most common hair-related issue is male-pattern baldness, often triggered by androgenic alopecia. Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) may reduce hair loss, but it doesn’t always reverse it. A hair transplant can provide a more feminine hairline and address receding hairlines or thinning hair.
Transgender Men (Assigned Female at Birth): Transgender men may experience hair thinning or a lack of facial hair due to hormone therapy. For some, growing facial hair is a significant step in aligning their appearance with their gender identity. Hair transplants can be used to create a fuller, masculine hairline or even facilitate the growth of facial hair.
In both cases, hair transplant procedures can be a crucial part of the gender-affirming journey, offering an effective solution for hair loss or reshaping one’s hairline.
Hair Transplant Basics
A hair transplant is a procedure that helps people grow hair in areas where it has fallen out or become thin. During the procedure, a doctor takes hair from one part of the scalp, usually the back, and moves it to a bald or thinning area. The new hair starts to grow in the new spot over time, just like natural hair. It is usually done with small tools, so there are no big cuts or scars. Hair transplants can help people feel more confident by giving them a fuller, thicker head of hair. It’s important to follow the doctor’s care instructions for the best results.
What is a Hair Transplant?
A hair transplant is a medical procedure in which hair follicles are taken from a donor area (typically from the back or sides of the scalp) and transplanted to an area of hair loss. The most common forms of hair transplants include:
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): This technique involves removing individual hair follicles from the donor area and transplanting them one by one to the recipient site.
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT): In this technique, a strip of tissue is removed from the donor area, and individual follicular units are dissected and transplanted.
Both techniques are effective, but FUE is generally preferred for transgender individuals due to its minimally invasive nature and quicker recovery time.
Common Hair Transplant Techniques
While FUE and FUT are the most commonly used methods, Direct Hair Implantation (DHI) and Robotic Hair Transplants are gaining popularity for their precision and minimally invasive nature.
For transgender individuals, FUE is often preferred due to its ability to create natural-looking hairlines with minimal scarring.
Hair Loss in Transgender Women (Assigned Male at Birth)
Hair loss in transgender women (assigned male at birth) can happen for different reasons. Many transgender women may experience hair thinning or baldness because of higher levels of male hormones, like testosterone, in their body. This is often called male pattern baldness. Some transgender women may also notice changes in their hair after starting hormone therapy, as the body adjusts to new levels of estrogen. Hair loss can be a tough experience, but there are treatments available, such as hair transplants, medications, and special shampoos, that can help restore hair and boost confidence. Talking to a doctor can help find the best option.
Causes of Hair Loss in Transgender Women
- Genetics: The most common cause of hair loss in transgender women is genetic androgenetic alopecia. A genetic predisposition to hair loss can affect both transgender and cisgender women.
- Hormone Levels: While estrogen therapy helps slow down hair loss, it does not always reverse it. Testosterone blockers like spironolactone may help to reduce hair thinning, but their effectiveness varies.
Hair Transplants for Transgender Women
For transgender women, a hair transplant can help restore a feminine hairline and encourage more natural hair growth in thinning areas. A skilled surgeon can work with the transgender woman’s specific goals, helping to design a hairline that complements their facial features and gender identity.
The procedure typically takes several hours and involves multiple sessions depending on the extent of the hair loss. Results may take anywhere from 6 months to a year to become fully visible.
What to Expect Before a Hair Transplant
Before a hair transplant, you will have a consultation with your doctor. During this meeting, the doctor will ask about your health and hair loss history. They will also talk to you about your goals for the transplant and design a plan just for you. The doctor might take pictures of your scalp and discuss options for the transplant procedure. You may be asked to stop taking certain medications before the surgery to prevent any issues. On the day of the transplant, the doctor will explain everything to you and make sure you feel comfortable and ready.
Consultation and Assessment
During the initial consultation, a board-certified surgeon will assess your hair loss pattern, skin quality, and overall suitability for a transplant. For transgender individuals, the surgeon will take into account their specific goals for hair restoration—whether that’s creating a feminine hairline or enhancing facial hair.
Pre-Operative Preparation
- Stop Certain Medications: You may be instructed to stop taking blood-thinning medications, like aspirin, in the weeks leading up to the procedure.
- Avoid Smoking and Alcohol: Smoking and alcohol can impair the healing process, so it’s advisable to avoid them at least a few days before the procedure.
- Hair Shaving: Depending on the method, the surgeon may need to shave the donor area or the entire scalp.
The Hair Transplant Procedure
The hair transplant procedure is a way to move hair from one part of your scalp to another. First, the doctor will numb the area with a special medicine so you don’t feel any pain. Then, they will carefully take hair from a thick-haired area, usually the back or sides of your head, and move it to the thinning or bald spots. The doctor will use tiny tools to make small cuts and place the hair follicles in the right places. The procedure usually takes a few hours, and you can go home the same day. Your hair will start to grow in a few months.
Step-by-Step Guide to the Procedure
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is administered to the donor and recipient areas to minimize discomfort during the procedure.
- Harvesting Hair Follicles: In FUE, individual follicles are removed one by one from the donor area. In FUT, a strip of tissue is removed and dissected into individual follicular units.
- Implantation: The follicles are then transplanted into the recipient area (the thinning or balding areas).
- Bandaging: The scalp is bandaged, and the patient is allowed to rest post-procedure.
Recovery Process
Recovery after a hair transplant usually takes a few days to a week. Patients are advised to avoid strenuous activities, direct sun exposure, and touching the transplanted area for the first few days. It can take several months for the transplanted hair to begin growing, and full results may take up to a year.
Post-Transplant Care and Results
After a hair transplant, it’s important to take good care of your scalp to get the best results. For the first few days, you might feel some soreness or swelling, but this will go away soon. You should avoid touching or scratching your scalp, and follow your doctor’s instructions for washing your hair gently. It’s also important to avoid direct sunlight and strenuous activities for a few weeks. Over time, the transplanted hair will start to grow. It can take several months for the new hair to become thick and natural-looking, so be patient and continue following your doctor’s care advice.Immediate Aftercare
After the transplant, it’s crucial to follow the surgeon’s post-op instructions. This may include:
- Medications: Pain relievers and antibiotics may be prescribed to prevent infection and manage discomfort.
- Washing the Scalp: The scalp must be washed gently, and hair care products should be mild and non-irritating.
Long-Term Hair Growth Expectations
Hair growth typically begins about 3 to 6 months after the procedure. Full results are generally visible within 12 months, and hair continues to thicken and mature over time. Transgender individuals can expect a natural, gender-affirming appearance, whether it’s a fuller hairline or more facial hair.
Potential Challenges for Transgender Individuals
Transgender individuals may face some challenges in life that others might not experience. One challenge is finding doctors who understand their needs, especially when it comes to things like hormone treatments or surgeries. Another challenge is dealing with changes in their body, such as hair loss, skin changes, or voice changes. Transgender individuals may also experience emotional struggles because of how society treats them or because of how they feel about their appearance. It’s important for transgender people to find support from family, friends, and healthcare professionals to help them through these challenges and feel confident in who they are.
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) and Its Effects
While HRT can promote facial hair growth in transgender men and help soften features in transgender women, it’s important to note that the effects of testosterone or estrogen on hair growth can vary from person to person. A hair transplant might be an essential step in achieving the desired hair growth when hormones are not enough.
Scalp Considerations in Transgender Patients
Scalp health can be a concern for transgender individuals, especially those on long-term HRT. Hair transplant surgeons must take into account skin thickness, elasticity, and the effect of hormone therapy on the scalp.
Financing and Insurance for Hair Transplants
Financing and insurance for hair transplants can be tricky, as not all insurance plans cover the cost. Hair transplants are often considered a cosmetic procedure, so insurance may not pay for it. However, some insurance plans might help if hair loss is caused by a medical condition, like alopecia. If your insurance doesn’t cover the transplant, you can ask the clinic if they offer payment plans or financing options. Many clinics allow you to pay in smaller amounts over time. It’s a good idea to talk to your doctor or clinic about costs and ways to make the procedure more affordable.
Is a Hair Transplant Right for You?
A hair transplant might be right for you if you’re struggling with hair loss and want to improve your hairline or fullness. It’s a good option if other treatments, like medications or shampoos, haven’t worked. Before deciding, it’s important to talk to a doctor who can help you understand the process and if it’s the right choice for you. The doctor will consider things like your health, age, and hair loss pattern. If you’re looking for a more permanent solution to hair loss and are willing to be patient as your hair grows back, a transplant could be a good option.
Conclusion
A hair transplant can be a life-changing procedure for transgender individuals seeking to achieve a more gender-affirming appearance. Whether you are looking to restore a feminine hairline or grow facial hair, a hair transplant can help. By understanding the process, expectations, and potential challenges, you can make an informed decision about this important step in your gender-affirming journey.
Always consult with a qualified, experienced surgeon who understands the specific needs of transgender patients. With the right care, you can achieve natural, long-lasting results that enhance both your appearance and your confidence.
